
The prostate is an organ that only men have. It is a smooth-surfaced gland that is part of the male reproductive system. It should generally be the size of a walnut, although this size varies over time. In many men, size begins to increase as they age between 40 and 50. The prostate can suffer from different disorders, including enlargement. That is what we have come to talk about today, about prostatitis.
In this article we will treat this disease in depth and you will be able to know the causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention. Do you want to know everything about prostatitis? Read on and find out everything.
Causes and symptoms of prostatitis

The prostate is located below the bladder and surrounds the urethral tube. Thanks to hormones, it is able to secrete a milky secretion that mixes with sperm during ejaculation. Some studies reveal that it is possiblee is part of 10% of seminal fluid.
The cause of prostatitis is diverse and depends on the pathogen that has caused its inflammation. It may or may not be bacteria. To find out if your prostate is swollen, there are various symptoms that can guide you to find out. These are:
- Burning, stinging, or stinging sensation when urinating (dysuria).
- Polyakiuria (frequent urge to urinate).
- Blood in the urine.
Depending on whether the cause of prostatitis is bacterial in origin or not, there are different symptoms. Although they may be different, they both share behaviors like those mentioned above.
When you have prostatitis you can have a fever and chills whatever time of year it is. If it is caused by a bacterium, other symptoms can be had such as:
- Discomfort in the testicles.
- Painful ejaculation
- Sensation of pressure and / or pain in the pubic region and lower abdomen.
- Pulling and pain in the groin.
- Erectile dysfunction.
- Loss of livid.
Therefore, if you have any of these symptoms, it is better to see your doctor as soon as possible.
Prevention and types
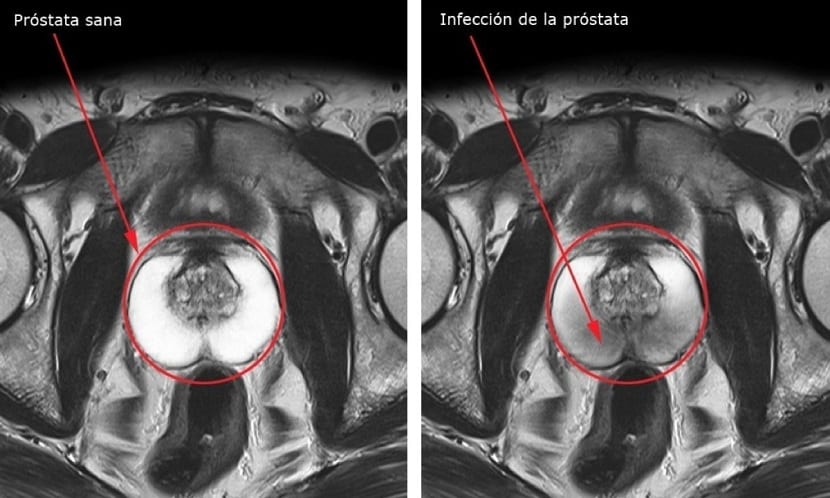
Not all types of prostatitis can be prevented. As usual, good hygiene and early medical treatment can prevent bacteria to spread to the prostate and cause its inflammation.
To learn more about which ones we can prevent and which ones we cannot, we are going to analyze all types of prostatitis. It can be divided into two large groups depending on the cause that has caused the inflammation. As we have said before, we can divide it into bacterial and non-bacterial prostatitis.
Bacterial prostatitis

The first is caused by the infection of a bacterium. This disease can be both acute and chronic. In both cases, certain bacteria enter the prostate and cause infection. In response to this, the prostate becomes inflamed and the aforementioned symptoms begin to suffer. The acute starts quickly, but the chronic would last three months or longer.
Diagnosis in acute prostatitis is easier to recognize than chronic prostatitis, since symptoms are seen more quickly. The treatment that is offered to you is, in general, taking antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection.
Any bacteria can cause a urinary infection producing acute bacterial prostatitis. Although it is not well known, some of the sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia and gonorrhea can cause prostatitis.
In men older than 35 years the bacteria Escherichia coli They can cause these types of diseases like other bacteria. This disease can lead to:
- The epididymis: tube that connects the testicles with the vas deferens through which the semen and sperm circulate.
- The urethra: tube that leads urine out of the body through the penis.
Acute prostatitis can also be caused by problems such as:
- An obstruction that reduces or prevents the flow of urine out of the bladder.
- Injury in the area between the scrotum and the anus (perineum).
With the use of medications, it usually disappears over time. If it is not treated well and precautionary measures are taken, it can recur to become chronic.
Abacterial prostatitis
The second is not an infection caused by any bacteria. Simply it can be due to disturbances in the emptying of the bladder or a prostatic reflux. There are some causes that cause it and they are:
- A constant reflux that comes from the urine and that flows to the prostate. This causes irritation.
- Some chemicals that cause irritation.
- Pelvic floor muscle problems
- Emotional factors that trigger stress.
To treat this type of prostatitis, it is best to control the symptoms. Treatment is quite difficult. If it is not treated in time, it can trigger other problems that affect lifestyle such as urinary or sexual.
Even if you get a medical checkup, nothing unusual is revealed. However, the prostate may be swollen. To know if it is inflamed or not, it is more advisable to do a urinalysis. To know the concentration of white and red blood cells you can know the state of the prostate. It is important to know that a utoculture or prostate culture does not show the presence of bacteria.
Diagnosis and treatments
Many mistakes are made in its diagnosis. Sometimes a sexually transmitted disease is diagnosed when you have prostatitis.
Regarding treatments, experts recommend a course of oral antibiotics for both types for about 4-6 weeks. If necessary, it would lengthen the time of the doses. If the patient must be hospitalized, it is more efficient to take antibiotics through the use of serum.
To combat pain, anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen or naproxen may be prescribed. It is important not to forget that the infection may not go away completely with the use of antibiotics. Therefore, it is better to prevent.
To treat him well it is recommended:
- Urinate frequently and completely.
- Take lukewarm baths to relieve pain.
- Avoid spicy foods, alcohol, caffeinated foods and drinks, or citrus juices.
- Drink between 2 to 4 liters of water approximately.
I hope that with this information you can learn more about this disease and its treatment.